CIVIL ENGINEERING
In the very first line, it should be clear to all of you that civil engineering is not just about the construction of buildings, bridges, railways, or megastructures ( dams, power projects, high-rise towers, etc.), it is way more than this.
Civil engineering is a way more explorable, vast, interesting, researchable, and backbone of any nation.
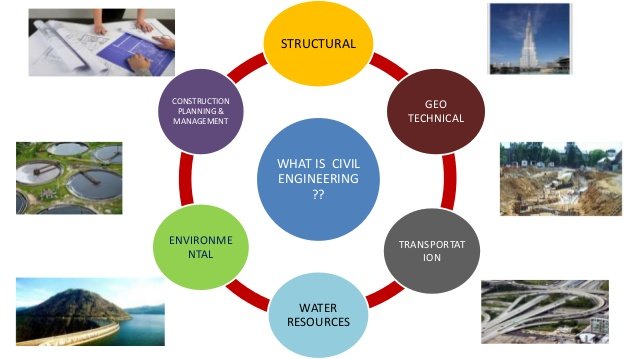
What is Civil Engineering?
One of the oldest and broadest engineering disciplines, Civil Engineering involves planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and supervising infrastructures which include facilities essential to modern life like highways, bridges and tunnels, schools, hospitals, airports, and other buildings, sewage systems, and water treatment facilities. Subsequently, the course also involves protecting the public and environmental health as well as improving existing infrastructure.
Civil engineering is the design, implementation, and maintenance of public works. This involves facilities and structures such as arenas, large-scale monuments, government buildings, transportation routes as well as other structures. Engineers will either work for the city or for a private firm that has been hired by the city. Some civil engineers work in the private sector on projects for independent companies. There are several types of civil engineering. A civil engineer can specialize in a number of different civil engineering branches. Those branches are described briefly below:
- Structural Engineering
- Geotechnical Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Transportation Engineering
- Water Resource Engineering
- Earthquake Engineering
- Material Engineering
- Construction Engineering
- Surveying
- Municipal Engineering
- Coastal Engineering
- Tunnel Engineering
Structural Engineering

This branch of civil engineering encompasses the structural analysis and design of structures. It is the responsibility of the structural engineer to analyze and design a structure that will safely bear or resist the stresses, forces, and loads. The design must satisfy the project specifications while meeting all safety regulations. The structure must endure massive loads as well as natural disasters and climate changes.
Major specialties:
- Earthquake engineering, the behavior of structures subject to seismic loading
- Wind engineering, the analysis of wind and its effects on the built environment
- Architectural engineering, application of engineering principles to building design and construction
- Ocean engineering, the design of offshore structures
Geotechnical Engineering

In geotechnical engineering, the engineer studies soil, foundations, and bearing capacities. The engineer will study the behavior of the earth materials and how they will affect a structure that is to be constructed. They will also evaluate pre-existing structures that are showing signs of problems with the earth materials under or near the structure.
Major specialties:
- Mining engineering, the exploration, extraction, and processing of raw materials from the Earth
- Foundation (engineering), the engineering of below-ground foundations that support superstructures
Environmental Engineering


This civil engineering type is the study of environment-friendly designs, pollution, and their resolutions and sewage management. Many engineers focus solely on the crisis of pollution and coming up with solutions as well as determining new and inventive ways for sewage management and other environmental entities.
Major specialties:
- Ecological engineering, the design, monitoring, and construction of ecosystems
- Fire protection engineering, the application of engineering to protect people and environments from fire and smoke
- Sanitary engineering, the application of engineering methods to improve sanitation of human communities
- Wastewater engineering, Wastewater engineering is a type of engineering that comes from civil engineering and environmental engineering. A wastewater engineer determines the best way to transport or collect rainwater for human populations. Wastewater engineering also deals with the transportation and cleaning of blackwater, greywater, and irrigation water. Wastewater treatment and water reclamation are areas of concern in this field. Wastewater engineers map out topographical and geographical features of Earth to determine the best means of collection. They use sonar scanning in wells to determine volumes of water that can be used for human consumption. Using these types of data they are able to provide a means of collecting water. After collecting the water, it is their job to transport it to where it can be made available for use.
- Municipal or urban engineering, civil engineering applied to municipal issues such as water and waste management, transportation networks, subdivisions, communications, hydrology, hydraulics, etc.

Civil engineers that specialize in transportation engineering will work with the planning, construction, and management of transportation facilities. They will design and implement the infrastructures that deal with transportation in order to provide a safe, comfortable, convenient, economical, and environmentally compatible mode of transport. There are six divisions related to transportation engineering: highway, air transportation, waterway, aerospace, coastal & ocean, and urban transportation.
Major specialties:
- Traffic engineering, a branch of transportation engineering focusing on the infrastructure necessary for transportation
- Highway engineering, a branch of engineering that deals with major roadways and transportation systems involving automobiles. Highway engineering usually involves the construction and design of highways
- Railway systems engineering
Water Resource Engineering

These engineers deal with the design and construction of hydraulic structures. These structures include dams, canals, and a water distribution system. The engineer is responsible for the design of the structure as well as the implementation and safety precautions that must be closely adhered to when dealing with hydraulic structures.
Major specialties:
- Hydraulic engineering, concerned with the flow and conveyance of fluids, principally water; intimately related to the design of pipelines, water supply network, drainage facilities (including bridges, dams, levees, channels, culverts, storm sewers), and canals.
- River engineering is the process of planned human intervention in the course, characteristics, or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit—to manage the water resources, to protect against flooding, or to make passage along or across rivers easier.
- Coastal engineering, the study of the processes ongoing at the shoreline and construction within the coastal zone, often directed at combating erosion of coasts or providing navigational access.
- Groundwater engineering involves the analysis, monitoring and often modeling of groundwater sources to better understand how much remains and if the water can be used for e.g. recharging reservoirs and irrigation.
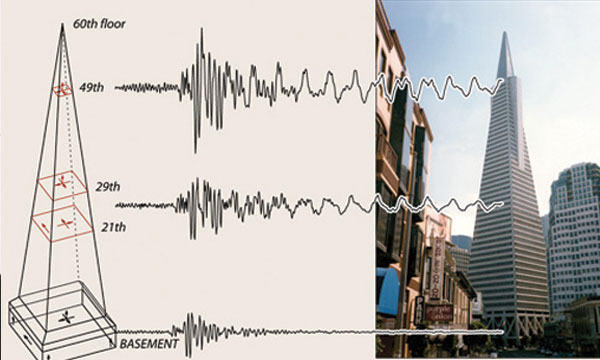
Earthquake Engineering
Earthquake engineers study the seismic forces and earthquake-resistant structures. In regions that are known for seismic activities, engineers must design and construct structures based on how well they will react within an earthquake situation.
Material Engineering
This branch of civil engineering deals with the study of material strength, properties of materials used in construction, and ceramics. These engineers will determine the best possible materials to be used for a project based on that project’s specifications.
Construction Engineering

This civil engineering branch deals with the planning, construction, and maintenance of structures. Construction engineering is the planning and execution of designs from site development, environmental, structural, transportation, and structural engineers. They must ensure that the plans that have been designed by other engineers are implemented to their exact specifications. Construction engineers will supervise fieldwork during the entire project. They are in a sense a cross between an engineer and manager as they will oversee the project from start to finish and handle any problems that come up throughout the duration of the project.
Surveying

This type of civil engineering branch handles the surveying and leveling of land by using different instruments to map and contour the terrain. This is done to locate and measure property lines, lay out buildings, bridges, channels, highways, and pipelines for construction. Surveyors are generally classified into two categories: plane surveying and geodetic surveying.
Municipal Engineering

These engineers will work with urban or city governments on the planning and management of the township. Most of these engineers work directly with government officials to ensure that the structures within the municipality are properly designed and implemented.
Coastal Engineering

This branch of civil engineering deals with coastal and marine structures. These structures include groins and embankments. These engineers not only ensure that the structures being erected correctly but they are also concerned with not disturbing the coastal regions.
Tunnel Engineering
Civil engineers who specialize in tunnel engineering are responsible for the planning, designing, construction, safety, and maintenance of tunnels. There are specifications that must be adhered to when working with tunnels for roadways, waterways, or trains.
Comments
Post a Comment